Arthroscopic Debridement
Arthroscopic Debridement Treatment
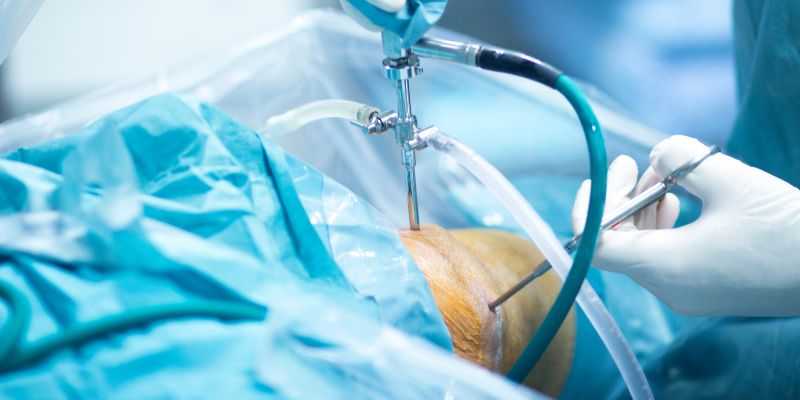
Treatment Range Hospital in Hyderabad offers advanced arthroscopic debridement procedures for the knee, ankle, and shoulder joints. This minimally invasive technique is used to clean out damaged cartilage, loose bone fragments, and inflamed tissue within the joint to relieve pain and improve movement. Ideal for early-stage arthritis, joint injuries, or post-traumatic inflammation, our expert orthopedic surgeons use state-of-the-art arthroscopy equipment to ensure safe and effective results.
The procedure is performed through tiny incisions using a camera and specialized tools, allowing for precise cleaning and minor repairs without disturbing healthy tissues. Arthroscopic debridement is commonly recommended for patients with joint stiffness, swelling, or mechanical symptoms like locking and catching. With shorter recovery times and less post-operative pain, it’s a preferred solution for many joint issues.
If you’re looking for arthroscopic joint cleaning in Hyderabad, Treatment Range Hospital provides expert orthopedic care, modern facilities, and customized rehabilitation programs. Whether it’s the knee, ankle, or shoulder, our minimally invasive approach ensures quicker healing and long-term joint relief.
- Your 6 - Phase health Process
Your Complete Arthroscopic Debridement Journey
🩺 Phase 1: Symptoms Identification
- Joint pain during movement or at rest
- Clicking, catching, or grinding in the joint
- Swelling or stiffness in the knee, ankle, or shoulder
- Limited range of motion or joint instability
- Symptoms unresponsive to medications or physiotherapy
🔬Phase 2: OPD Consultation with Orthopedic Surgeon
- Clinical evaluation of joint mobility and stability
- Detailed history of symptoms, injuries, or arthritis
- Imaging tests: X-ray (for bone), MRI
- Discussion on conservative vs. minimally invasive surgical approach
📝 Phase 3: Causes (Etiology)
- Degenerative joint disease
- Sports injuries or repetitive joint strain
- Trauma or fall causing joint surface damage
- Synovitis or chronic inflammation of joint lining
- Loose cartilage, bone spurs, or scar tissue in the joint
🔧Phase 4: Diagnosis & Surgical Planning
- Imaging and symptoms confirm need for debridement
- Procedure aims to:Remove loose bodies
- Smooth rough cartilage surfaces,Flush out inflammatory debris
- Surgical planning includes pre-anesthetic evaluation and physiotherapy prep
- Education on recovery time, expectations, and precautions
💊 Phase 5: Treatment – Arthroscopic Debridement Procedure
- Performed via tiny incisions using an arthroscope and instruments
- Joint is cleaned, and damaged tissue is trimmed or removed
- Saline is used to irrigate and flush the joint
- Duration: 30–60 minutes; mostly day-care procedure (same-day discharge)
- Small dressings applied; joint may be wrapped or braced temporarily
💪 Phase 6: Post-Surgery Care & Recovery
- Ice, rest, and elevation to reduce swelling
- Crutches may be used temporarily for lower limb procedures
- Physiotherapy starts early for mobility and strength
- Return to light activities: 1–3 weeks
- Avoid high-impact activity for 4–6 weeks
- Follow-up visits to monitor healing and function improvement
Insurance Support










- Why Choose Us
Why patients trust us with their care
- Patient Testimonials
Patient stories of care and recovery










- Frequently Asked Questions
Helping you understand Our healthcare
Arthroscopic debridement is a minimally invasive surgical procedure where a small camera and specialized tools are used to “clean out” a joint by removing loose cartilage, inflamed tissue, or bone fragments.
This procedure is most commonly performed on:
Knee
Ankle
Shoulder
It may also be used in the elbow, wrist, or hip in select cases.
Joint pain, especially during movement
Swelling and stiffness
Clicking, catching, or grinding sensations
Locking or decreased range of motion
Pain not responding to medication or physical therapy
Early osteoarthritis
Synovitis (inflamed joint lining)
Cartilage fraying or loose bodies
Meniscal or labral fraying
Post-traumatic joint debris
Your surgeon will use:
Physical examination
X-rays to check joint alignment and bone condition
MRI or ultrasound to assess cartilage, tendons, and soft tissue damage