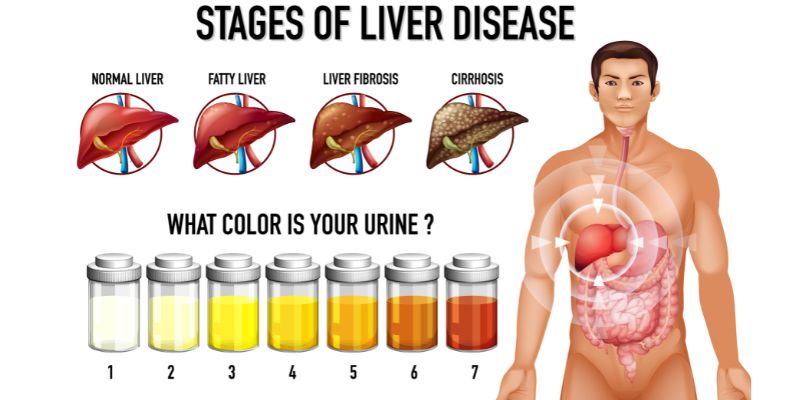
Fatty Liver / NAFLD / NASH
Fatty Liver / NAFLD / NASH Treatment
Treatment Range Hospital in Hyderabad offers specialized care for patients suffering from Fatty Liver Disease, including NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) and NASH (Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis). Our experienced hepatologists and gastroenterologists provide comprehensive evaluation and treatment plans tailored to manage and reverse liver fat accumulation, inflammation, and damage. We are recognized among the best hospitals in Hyderabad for fatty liver management using evidence-based approaches.
Our team focuses on early diagnosis through blood tests, liver function analysis, ultrasound, FibroScan, and lifestyle assessment. Depending on the stage of liver disease, we offer personalized medical and nutritional therapies, weight management programs, and long-term monitoring to prevent progression to cirrhosis or liver failure. For patients with metabolic conditions like diabetes or obesity, we offer integrated care to address root causes of NAFLD and NASH effectively.
If you are searching for fatty liver treatment in Hyderabad, Treatment Range Hospital provides ethical, affordable, and expert care under one roof. With advanced diagnostics, skilled specialists, and a strong focus on prevention and recovery, we help patients take control of their liver health and overall well-being.
- Your 6 - Phase health Process
Your Complete Fatty Liver / NAFLD / NASH Treatment Journey
🔍 Phase 1: Symptom Identification
- Often silent with no symptoms in early stages
- Fatigue or weakness
- Unexplained weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Mild right upper abdominal discomfort
- Elevated liver enzymes on routine blood tests
- May be associated with obesity, diabetes, or high cholesterol
🩺 Phase 2: Consultation with Hepatologist or Gastroenterologists
- Detailed review of medical history and risk factors
- Physical exam including BMI, waist circumference, and blood pressure
- Discussion about lifestyle, diet, alcohol intake, and medications
- Education on progression risk: NAFLD → NASH → Cirrhosis
🔬 Phase 3: Diagnosis
- Blood tests: Liver function tests (ALT, AST), lipid profile, HbA1c
- Imaging: Ultrasound, FibroScan (elastography), or MRI
- Rule out viral hepatitis, autoimmune hepatitis, and alcohol-related liver disease
- Liver biopsy (if needed) to confirm NASH or assess fibrosis severity
- Grading of disease severity to tailor treatment
🛠️ Phase 4: Treatment Planning
- Focus on gradual, sustained weight loss (5–10% of body weight)
- Diet: Low-carb, Mediterranean, or plant-based diet recommended
- Physical activity: At least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week
- Diabetes, hypertension, and high cholesterol
- In select cases, vitamin E or medications may be prescribed
📈 Phase 5: Monitoring & Follow-Up
- Regular follow-ups every 3–6 months
- Repeat liver function tests and FibroScan as needed
- Track weight, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels
- Adjust treatment plan based on response and compliance
- Ongoing motivation and lifestyle coaching may be provided
🏥 Phase 6: Long-Term Prevention & Liver Care
- Avoid alcohol and smoking
- Maintain long-term healthy eating habits
- Continue regular physical activity
- Annual liver check-up for at-risk individuals
- With commitment, NAFLD and early NASH are reversible — preventing liver failure or cancer
Insurance Support










- Why Choose Us
Why patients trust us with their care
- Patient Testimonials
Patient stories of care and recovery










- Frequently Asked Questions
Helping you understand Our healthcare
Fatty liver disease is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. It can be caused by alcohol (alcoholic fatty liver) or by other factors like obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease or NAFLD).
NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) is the early stage of fat accumulation in the liver without significant inflammation or damage.
NASH (Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis) is a more severe form of NAFLD, where the liver becomes inflamed and can progress to fibrosis, cirrhosis, or liver cancer.
Low or no urine output
Swelling in feet, ankles, or face
Nausea, vomiting, or poor appetite
Confusion or drowsiness
Difficulty breathing
High blood pressure or chest discomfort
Diagnosis is made through:
Blood tests to check liver enzymes
Imaging such as ultrasound, FibroScan (elastography), or MRI
Liver biopsy (in some cases) to confirm NASH or fibrosis
Typically every 3–6 months, depending on disease severity. Follow-ups include blood tests, lifestyle review, and imaging if needed to monitor disease progression or improvement.